Decomposition in Project Management
What Picasso said for the art,
“Every act of creation begins with an act of destruction”
goes for project management too. To begin the project, developers usually split it into smaller chunks. Decomposing your project decreases the uncertainty and makes the project more understandable.
Let’s talk more specifically about decomposition in project management!
What is Decomposition in Project Management?
As we already mentioned, decomposition in project management is splitting the project into smaller chunks. These chunks should be manageable, controllable, and achievable. Decomposing the project is a technique for dividing and subdividing the project scope. The scope is usually divided into units of work called sprints. Further, each sprint is then divided into user stories.
The number or complexity of work units or work packages depends on the size of the project. Now, if the project is enormous, not that the work on it will take time, but also the assigning work packages to different team members will.
Decomposition in Project Management throughout WBS
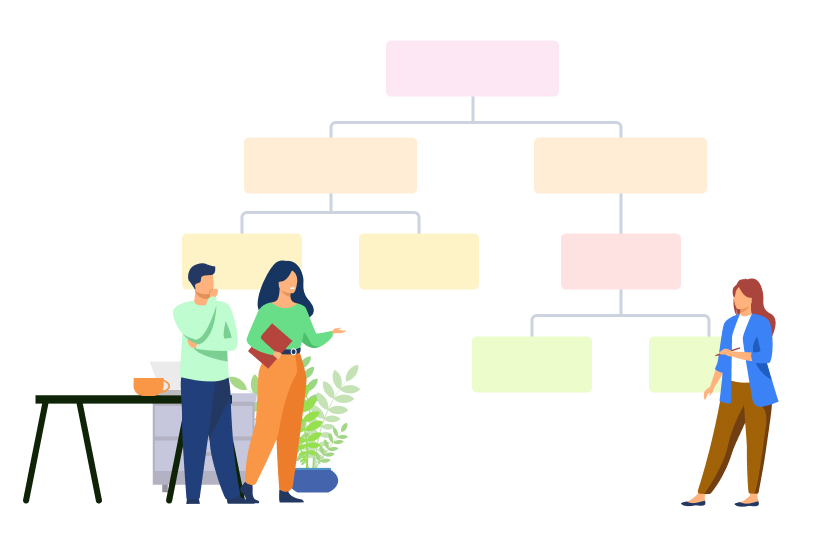
That process can be shown graphically and then we call it Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Except for units of work, WBS helps understand the flow of budget and schedule.
There are many differentiations on how to use WBS in your projects. One of the ways to differ WBS structures is to differ top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Top-Down WBS
The top-down approach begins with the overall project. Then, the overall project contains into sub-projects or lower-level projects. We are focusing on general project characteristics and not specifications. The dividing tasks into smaller ones continue until we don’t create concrete work units.
Since it is more logical first to define a problem and then a solution, this approach is more popular. Learning the big picture first and afterward the details works better for most. However, there are some teams that prefer the other way round.
Bottom-Up WBS
The bottom-up approach begins with smaller tasks that team members suggest. These small tasks have goals together to make the project. Members are submitting low-level tasks that they think would help in finishing the project. This approach is complex for a team where not all team members have the same technical knowledge.
Process-oriented
Process-oriented WBS is a kind of WBS that defines a project with phases, steps, and functions. Steps are described with individual discipline that should finish the project. If you are using it together with deliverables-oriented WBS, it shows a functional perspective. It can also enable setting the high-quality processes throughout the project.
Deliverables-oriented
A deliverables-oriented WBS decomposes the project into tangible deliverable components. Here, deliverables are usually a physical component of the whole project. This kind of WBS is useful to project managers to have a view of the scope. The overview of related deliverables helps to estimate costs and resources to various management levels.
The Importance of Decomposition
Even if you work on a small project and you think you figure it all out, you still need to decompose it. Here are reasons why:
Budget plan
Cost estimates are one of the first things you should have for the project. The role of a project manager is to make a cost plan as soon as possible.
Resources plan
To know the budget, you should know your resources first. That means you should decompose your project to that level that is possible to define what resources you will use.
Project schedule
After budget and resources, you need to think about the deadlines. The project schedule shows how work is divided by work units.
How to decompose your project
There are many ways to decompose your project. One of the visual methods is WBS. The top-down approach in WBS will make clear decomposition from the big picture to specific tasks.
Identify deliverables
Every project has deliverables. They are the wanted outcomes of the work. In project management, deliverables can be specifications, functionalities, and features. A deliverable should be within the project scope. It is also related to finishing the project’s objectives.
Project deliverables should be clear to all team members. Stakeholders review them as well so it’s important that they are clear. In other words, the absence of clearly defined deliverables is one of the causes of delays in project management.
Work on each delivery individually
It is important to split all different deliverables. You can differ them based on the product part of the resources. After you define them, break down each one of them into clear features. The number of features will depend on the project complexity. Every feature can further be divided into work packages.
In general, work packages should be simple enough that each of them can be done by one team member.
Estimate dates
After defining deliverables, it is necessary to organize them in work packages. Estimating the amount of time for each work package is an important part of decomposition. One work unit, according to Joseph Phillips shouldn’t exceed 8 hours of work. To clarify, the more specific the evaluation is, the better you could improve your sprint velocity.
Estimate cost
Estimating the cost of every task will help more precise project estimation. Costs depend on task duration and the resources that they require. After estimating the costs, deliverables are ready to decompose with a break-down structure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, to create a product, first what you need to do is decompose the plan into smaller parts. This process requires good project management skills and knowledge. A project manager should think about many of the divisions to get things done in the right way.
As has been noted, WBS is one of the most useful and easy-to-use parts of decomposition. However, there is still a lot going on to overcoming decomposition challenges. JadeALM can be a solution for you. It provides easy-to-follow WBS and a single source of truth that frees your manual updating of the changes in WBS.
Try it out for free and let us know how did you like it.



